What is Geofoam ?
¡ Geofoam is expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS) manufactured into large lightweight blocks.
¡ The primary function of geofoam is to provide a lightweight void fill below a highway, bridge approach, embankment or parking lot.
¡ EPS Geofoam minimizes settlement on underground utilities.
¡ EPS Geofoam is used widely as compared to XPS Geofoam.
¡ Since the manufacturing of XPS causes emissions of CFCs and HFCs harmful to the nature.
Geofoam Blocks
¡ The blocks vary in size but are often 2 m x 0.75 m x 0.75 m.
APPLICATIONS
¡ SLOPE
STABILIZATION:
To
reduce the tendency of failure of portion of the soil, the crest of the slope
is excavated and replaced by the super lightweight material EPS geofoam.
¡ Alternative
solutions:
•
Changing of the slope inclination,
•
Buttressing the toe of the embankment using
soil nailing
•
Any other solution that may affect the
geometry of the slope or the surrounding land or may not be feasible for many
reasons.
¡ REDUCING
LATERAL PRESSURE ON RETAINING STRUCTURES
•
To reduce:
ü
static earth pressure acting behind an
abutment during and after construction of the backfill
ü
the dynamic earth pressure due to
earth-quakes and traffic loads after the construction
•
Finite element analysis, showed 85% reduction
in the overall bending moment when utilizing 12kg/m3 EPS geofoam.
•
The 20kg/m3 geofoam showed 70% reduction
compared with the case of no geofoam.
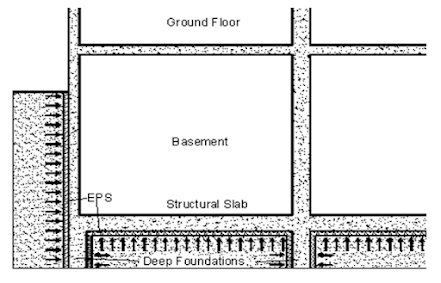
COMPRESSIBLE INCLUSION
AGAINST EXPANSIVE SOIL
¡ Expansive
soils or swelling soils are those soils that have the tendency to increase in
volume when water is available and to decrease in volume if water is removed.
¡ Upon
soil heave EPS geofoam compresses according to its own stress strain relation.
¡ The
geofoam will also act as a form for the slab.
¡ EMBANKMENT
FILL TO REDUCE SETTLEMENT
•
Figure shows a situation of constructing a
new embankment on soft ground.
•
Large settlement can be experienced under the
load of the conventional embankment fill.
Existing utility line: damaged if not designed for large deflections.
¡ WIDENING EMBANKMENTS
•
The self-standing property will reduce the
additional space without the need of a retaining wall.
¡ STRESS
REDUCTION IN BURIED PIPES
•
The compressible inclusion of EPS geofoam may
be utilized to reduce loading above rigid conduits.
•
Thin layers of EPS geofoam are placed some
0.5m above the rigid conduit.
¡ PAVEMENT
AND RAILWAY INSULATION
•
The cycle of winter freezing and spring
thawing of soil can affect transportation facilities such as roads and
railroads.
•
This is because the ground surface heaves as
a result of freezing and settles upon thawing.
Geofoam for roadway
embankments as an alternative to ground improvement
¡ Maintenance
is not required.
¡ All
weather resistant.
¡ The
overall time for construction is typically much shorter and less.
¡ Saving
cost of heavy equipments.
¡ In
consideration of these benefits, the typically higher unit cost of geofoam is
usually more than offset by savings when overall project costs are
considered.
ADVANTAGES OF GEOFOAM
¡ Super
lightweight material
¡ Most
versatile lightweight materials available.
¡ Low density/ high strength: Geofoam
is 1% to 2 % the density of soil with equal strength.
¡ Predictable
behavior: Geofoam allows engineers to be much more specific in the design
criteria. This is very different than other lightweight fillers, such as soil,
that can be very variable in composition.
¡ Inert:
Geofoam will not breakdown, so it will not spread into surrounding soils, no leachates.
¡ Reused:
Geofoam can also be dug up and reused.
¡ Limited
labor required for construction: Geofoam can be installed by hand using simple
hand tools. This eliminates the investment and operating cost of heavy
machinery.
¡ Cuts
down on construction time: Geofoam is quick to install and can be installed
during any type of weather, day or night, resulting in faster installation
time. It can arrive at the job site prefabricated and ready to place and is
easily inventoried and handled.
¡ Installation
is not delayed by weather.
¡ It
maximizes onsite installation efficiency.
¡ Insect
and Mold Resistant
¡ Proven
Performance
¡ Maintenance
Free
¡ Contains
no CFC, HCFC, or HFC. Thus environment friendly.
DISADVANTAGES OF GEOFOAM
¡ Fire
hazards: Untreated Geofoam is a fire hazard.
¡ Vulnerable
to petroleum solvents: If Geofoam comes in contact with a petroleum
solvent, it will immediately turn into a glue-type substance, making it
unable to support any load.
¡ Buoyancy:
Forces developed because of buoyancy can
result in a dangerous uplift force.
¡ Susceptible
to insect damage: Geofoam should be treated to resist insect infestation. If it
is not, insects such as ants can burrow into the Geofoam, weakening the
material.
Present Scenario and Scope
¡ Has
been used around the world as a fill for more than 30 years.
¡ In
India, some industries manufacturing geotextiles also manufacture geofoam
blocks.
¡ However
use of geofoam is not seen on a large scale in India.
¡ Scope:
Soft soils in India are found near marine and river delta deposits.
Properties
• Density
• Compression
• Tension
• Creep
• Flexural
• Thermal Resistance
• Flammability
• Water Absorption
• Resistance to Attacks
• Durability
• Inertness Properties
• Energy Absorption
• Acoustical properties
• Environmental Effect
Density
¡ Can be considered to be the main index of its properties
¡ Cost of manufacture is considered proportional to density
¡ For practical civil applications it ranges between 11 and 30 kg/m3
Compression
Tension
¡ Tensile
strength of EPS material can be an indication of the quality of fusion of the
prepuffs and any recycled EPS geofoam used in the process.
¡ It
increases with density widely used as a quality control test in EPS geo-foam
manufacturing plants
Flexure
¡ Widely
used as a quality control test in EPS geo-foam manufacturing plants.
¡ The
maximum stress is calculated assuming the material is linear elastic up to
failure.
¡ The
material fails in tension as a crack on the tension side appears at the moment
of failure.
Creep
¡ Susceptible
to time dependent creep deformation when a constant stress level is applied
¡ Dependent
on
§
Density -- the creep decreases as density
increases
§
Stress -- lower the stress, lesser is the
creep deformation
Thermal Resistance and Flammability
¡ Poor
conductor of heat and therefore excellent for heat insulation
¡ Combustible
Water Absorption
¡ Low
¡ Depends
on:
§
Density
§
Fusion
Resistance to Attacks
¡ Sensitive
to attack by solvents
¡ Most
acids and their water solutions do not attack polystyrene; however strong
oxidizing acids do
¡ Does
not attack ants, termites, etc but is not resistant to them
¡ Not
susceptible to fungal attacks and bacterial growth
Environmental Effect
¡ EPS
geofoam is made of polystyrene beads and polystyrene is not biodegradable and
chemically inert in both soil and water
¡ Does
not contaminate the ground and ground water
¡ Recyclable
material
¡ Does
not use CFCs or HCFCs in its manufacture like other polymeric foam
¡ Good
energy absorber,
¡ Inert
and does not attack metals in contact with it,
¡ Reduces
transmission of airborne sound
Design and Construction Considerations
¡ Buoyancy
¡ Concentrated
Loads
¡ Chemical
Attack
¡ Flammability
¡ Insect
Infestation
¡ Moisture
Absorption
¡ Gaps
Between Blocks
¡ Immediate
Deformation
¡ Connections
with Structural and Architectural Elements
¡ Sliding
¡ Blocks
Alignment
¡ Transition
Zones
|
Lightweight
Material |
Unit Volume Weight (tf/m3)* |
Description |
|
EPS Blocks |
0.01 ~ 0.03 |
Ultra lightweight, expandable synthetic resins |
|
Expanded
Beads Mixed Lightweight Soil |
0.7 approx. or more |
Variable density; similar compaction and deformation characteristics
to soil; can use excess construction soil |
|
Air Foamed
Mortar and Air Foamed Lightweight Stabilized Soil |
0.5 approx. or more |
Density adjustable; flow able; self-hardening; and can use excess
construction soil |
|
Coal Ash,
Granulated Slag, etc |
1.0 ~ 1.5 ap-prox. |
Granular material; self hardening |
|
Volcanic Ash
Soil |
1.2 ~ 1.5 |
Natural material |
|
Hollow
Structures |
1.0 approx. |
Corrugated pipes, box culverts, etc. |
|
Wood Chips |
0.7~ 1.0 |
Usually to be used below ground water level; anti leaching measures
needed |
|
Shells |
1.1 approx. |
Sized 12 to 76 mm; interlocking effects |
|
Tire Chips |
0.7~ 0.9 |
Usually used above ground water level; cover soil layer at least 0.9m
is required |
METHODS OF CONSTRUCTION
¡ Done
in reference with ASTM D7180
¡ SUBGRADE
PREPARATION:
1. Clear and grub
site.
2. Excavate existing soil if required.
3. At design engineer’s discretion, place geotextile over
graded surface, i.e. soft
soils, etc.
4. Dewater site as required.
5. Place a sand pad/leveling course over the prepared
surface of 50 mm thickness minimum. Sand pad surfaces should be above ground
water level at time of EPS Geofoam
placement.
¡ PLACEMENT:
1. Verify identification marks on face of the product.
Field sampling and testing of the Foam-Control EPS Geofoam will be as specified
by the Engineer. Properties of density and compressive resistance shall be
verified in accordance with the specification.
2. Material is placed as required by the engineer and as
shown on the drawings.
3. Blocks of Foam-Control EPS Geofoam should be placed
tightly on the prepared sand pad/leveling course. For multiple layers of Foam-Control
EPS Geofoam, successive layers of blocks are oriented at 90 degrees to previous
layer.
4. Geofoam must
receive temporary ballast during all phases of construction to prevent
displacement by wind or high water conditions.
5. In order to
facilitate construction during precipitation or when frost or icing is
encountered, horizontal restraint (Geogripper) between layers of EPS Geofoam
may be desired.
6. Commence with
the placement of permanent overlying materials as quickly as practical.
¡ Geogripper:
Plates used to restrain EPS Geofoam from moving laterally in layer over layer
applications. The plate shall be made of galvanized or stainless steel with
two-sided multi-barbed design capable of piercing geofoam. Each plate shall be
capable of a lateral holding strength of 60 lbs (approx 27 kgs)
















0 Comments
If you have any doubts, suggestions , corrections etc. let me know