Slope Management in Hill Roads and Landslides
Hill slopes across highways
A) Based on height
B) Base on slope inclination & presence of overhangs
C) Based on Geological classifications
Definition of Hill slopes across Highway
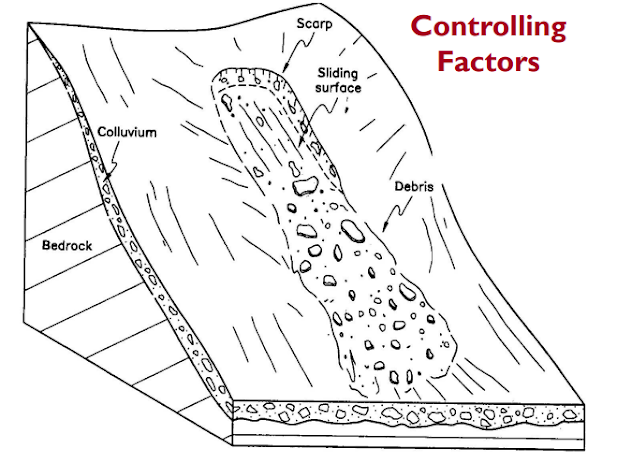
Convex slope segments commonly occur in the upper parts of soil man taled slopes, as near the drainage divideStraight slope segments are dominated by mass movement processes.
Talus slopes are a type in which debris piles up to a characteristic angle of repose.
When new debris is added to the slope, thereby locally increasing the angle, the slope adjusts by movement of the debris to re-establish the angle.
Concave slopes are especially common where overland-flow runoff transports sediment derived from upper slopes.
Virgin slopes
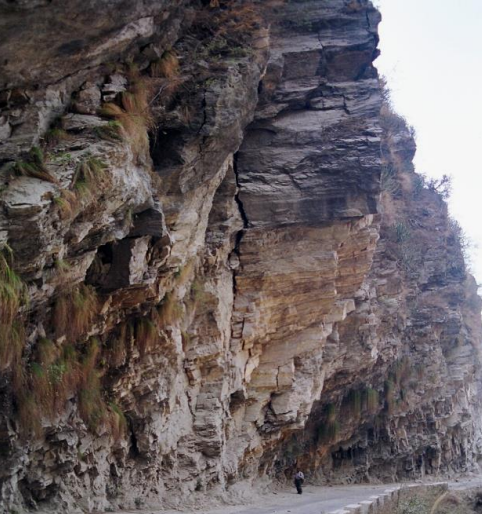
Highway cut slopes
Manmade slopes
Components of Hill Slope across Highways
Geological, Geomorphological, Geohydrological, Geotechnical, Ecological/Environmental Interactions and Interrelationships between Slope Components
Investigations of Hill Slopes & Processes
Geological Investigations - Type of material, structures
Identification of material,
A) Soil Strata ➢ Sandy soil ➢ Clayey soil
Residual soil
Talus
Colluviums
Moraines, glacial
Alluvium Loess
B) Rocky Strata ➢ Type of Rock ➢ Weathering extent ➢ Joint pattern
Joints
Faults
Folds
Fractures
C) Mixed Strata ➢ Mix of soil + boulders
Properties and classification
Geomorphological Investigations- type of slope, steepness and various features on the slope
Micro and macrofeatures of morphology
Erosion of slope -
Presence of streams -
Presence of waterfalls -
Presence of vegetation -
Extent of Erosion -
Piping phenomenon -
B) Rocky Strata ➢ Type of Rock ➢ Weathering extent ➢ Joint pattern
Joints
Faults
Folds
Fractures
C) Mixed Strata ➢ Mix of soil + boulders
Properties and classification
Geomorphological Investigations- type of slope, steepness and various features on the slope
Micro and macrofeatures of morphology
Erosion of slope -
Presence of streams -
Presence of waterfalls -
Presence of vegetation -
Extent of Erosion -
Piping phenomenon -
Geohydrological Investigations-Drainage network, springs, Rivers etc
Surface and Sub-surface Drainage Investigations,
Watershed Management
Geotechnical Investigations - Strength properties of the material
Seismic Refraction Tomography (SRT) :- This method utilizes the refraction of seismic waves on geologic layers -rock/soil units in order to characterize the subsurface conditions and geologic structure. Shots are deployed at surface and recordings are made using geophones.
Some natural phenomena that can trigger a landslide are
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and seismic shaking
Intense rainfall, rapid snowmelt, glaciers melting, and changes in water level
Stream/coastal erosion and natural dam failure
Rising of groundwater or increase of pore water pressure
The undercutting of cliffs and banks by water erosion due to tidal waves
Anthropogenic action
Highway Hill Slope Vulnerability and Risk Assessment
Highway hill slope rating system
Rating criteria for identification and classification of highway slopes
Suitability/vulnerability and potential for hill slope failure
Zonation of slopes :- Zonation of highway hill slopes based on their vulnerability classes (methods and applications)
Slopes
Man made slopes
Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and seismic shaking
Intense rainfall, rapid snowmelt, glaciers melting, and changes in water level
Stream/coastal erosion and natural dam failure
Rising of groundwater or increase of pore water pressure
The undercutting of cliffs and banks by water erosion due to tidal waves
Anthropogenic action
Highway Hill Slope Vulnerability and Risk Assessment
Highway hill slope rating system
Rating criteria for identification and classification of highway slopes
Suitability/vulnerability and potential for hill slope failure
Zonation of slopes :- Zonation of highway hill slopes based on their vulnerability classes (methods and applications)
Identification/estimation/calculation of risk due to vulnerable highway hill slopes
Terrain/Slope inventorySlopes
Man made slopes
Natural slopes
Rock slopes
Rock slopes
Soil slopes
Bedding controlled slopes
Geology
Discontinuities
Geology
Discontinuities
Slickensides surface
Weak materials e.g. clay seams
Colluvium- material characteristics
Alluvium – Characteristics
Ancient landslide
Slope morphology
Drainage morphology
Vegetation type
Slide type
Micro features on the slope
Cracks/fracturs/subsidence
Sinking/cavities
Bulging
Deformed ground
Break in slope
Hummocky ground
Drainage system
Micro features on the slope
Cracks/fracturs/subsidence
Sinking/cavities
Bulging
Deformed ground
Break in slope
Hummocky ground
Drainage system
Hydrology
Slope hydrology
Catchment
Ephemeral drainage
Topography vs Drainage flow
Scouring/Erosion
Rockfall
Slumps
Slides
Subsidence
Infrastructure
N. Highway
SH-MDR-VR
Railways
Irrigation Canals Dams etc.
Highway Hill Slope Protection Structures (Construction & Maintenance)
Stabilization of slopes-
Excavation at Top of Slope,
General Flattening of Slope,
Benching of Slope,
Complete Removal of Unstable Mass,
Earth Fill at Toe Slope,
Rock or Gravel Fill at Toe of Slope
By Replacing Existing Soil with Low density material, such as Geofoam
Application of Geosynthetics for hill slopes stabilizations
Selection of Structures for Protection-
Debris Arrestors,
Retaining Wall - PCC wall section Calculator
Selection of Structures for Protection-
Debris Arrestors,
Retaining Wall - PCC wall section Calculator
Rock and Earth Fill Buttress at Toe of Slope,
Cribs or Gravity Retaining Wall,
Breast Wall,
Toe Wall,
Pile Walls,
Benching,
Filter beds,
Easing of Slopes,
Bitumen/ Asphalt mulching,
Chutes and Sloping Aprons,
Turfing
Caisson Toe of Slope,
Barriers at Toe anchored by Tie- Back Method of increase of Shear Strength of Soil Cementation,
Cribs or Gravity Retaining Wall,
Breast Wall,
Toe Wall,
Pile Walls,
Benching,
Filter beds,
Easing of Slopes,
Bitumen/ Asphalt mulching,
Chutes and Sloping Aprons,
Turfing
Caisson Toe of Slope,
Barriers at Toe anchored by Tie- Back Method of increase of Shear Strength of Soil Cementation,
Freezing, Electro-Osmosis,
Compaction, Rock Bolting, Blasting at Toe
Note: - Maintenance of slope protections structures are equally important
Compaction, Rock Bolting, Blasting at Toe
Note: - Maintenance of slope protections structures are equally important
Drainage System, <-- click on link to read detailed article.
ATTRIBUTES/FACTORS for Slope Management Inventory
A- LocationB- Age of cutting
C- Type of slope
D- Mode of failure
E- Type of lithology
F- Thickness of soil/debris on affected slopes
G- Thickness of overburden
H-Vegetation on affected slope
I- Vegetation above beyond affected slope.
J- Height of cutting
K- Slope of cutting
L- Cut slope angle vs. Uphill natural slope.
M- Water conditions
N-Deformation characteristics (cracks/subsidence/failure)
O- Joint sets
P- RMR (rock slope)
Q- Direction of bedding plane/foliation
R- Natural Drainage Preservation
S- Type of Road --> Express way, National Highway, State Highway, MDR, ODR, VR, NP etc.
T- Number of Road
U- Chainage of Landslide location
Brief list of remedial measures for unstable slope
MODIFICATION OF SLOPE GEOMETRY✓ Removing material from the area driving the landslide (with possible substitution by lightweight fill)
✓ Adding material to the area maintaining stability (counterweight berm or fill)
✓ Reducing general slope angle
DRAINAGE
✓ Surface drains to divert water from flowing onto the slide area (collecting ditches and pipes)
✓ Shallow/deep trench drains filled with free draining geomaterials (coarse granular fills and geosynthetics)
✓ Buttress counter forts of coarse-grained materials (hydrological effect)
✓ Vertical (small diameter) boreholes with pumping or self-draining
✓ Vertical (large diameter) wells with gravity draining
✓ Sub-horizontal or sub-vertical boreholes
✓ Drainage tunnels, galleries or adits
✓ Vacuum dewatering
✓ Drainage by siphoning
✓ Electro-osmotic dewatering
✓ Vegetation planting (hydrological effect)
RETAINING STRUCTURES
✓ Gravity retaining walls
✓ Crib-block walls
✓ Gabion walls
✓ Passive piles, piers and caissons
✓ Cast-in situ reinforced concrete walls
✓ Reinforced earth retaining structures with strip/ sheet - polymer/metallic reinforcement element
✓ Buttress counterforts of coarse-grained material (mechanical effect)
✓ Retention nets for rock slope faces
✓ Rockfall attenuation or stopping systems (rocktrap ditches, benches,fences and walls)
✓ Protective rock/concrete blocks against erosion
INTERNAL SLOPE REINFORCEMENT
✓ Rock bolts
✓ Micro piles
✓ Soil nailing
✓ Anchors
✓ Grouting
✓ Stone/lime cement columns
✓ Heat treatment
✓ Freezing
✓ Electro osmotic anchors
✓ Vegetation planting (root strength mechanical effect)














0 Comments
If you have any doubts, suggestions , corrections etc. let me know